Aldi’s Business Model and Financial Performance
Aldi stock price – Aldi’s success is rooted in its distinct business model, characterized by a relentless focus on efficiency and cost reduction. This strategy, coupled with shrewd pricing and supply chain management, has propelled its impressive financial performance, allowing it to compete effectively against larger retail giants.
Aldi’s Business Strategy and Profitability
Aldi’s core business strategy centers around offering a limited selection of high-quality, private-label products at significantly lower prices than competitors. This “discount” model necessitates a streamlined operation, minimizing overhead costs through efficient store layouts, reduced staffing, and a highly optimized supply chain. This focus on efficiency directly translates into higher profit margins compared to retailers with broader product ranges and higher operational expenses.
Aldi’s Revenue Streams and Cost Structure
Aldi’s revenue primarily stems from the sale of its private-label grocery items, with a smaller contribution from non-food items. Its cost structure is remarkably lean, focusing on minimizing waste, negotiating favorable supplier contracts, and employing efficient logistics. A significant portion of cost savings is achieved through its highly efficient distribution network and store operations. Unlike many competitors, Aldi significantly reduces marketing and advertising costs, relying instead on word-of-mouth and reputation.
Comparative Financial Performance
While precise financial data for privately held Aldi is limited, publicly available information and industry analyses suggest Aldi consistently outperforms many of its competitors in terms of profit margins. Compared to publicly traded companies like Kroger and Walmart, Aldi’s operating profit margins are generally higher, reflecting its efficient business model. Direct comparison to Lidl, another discount retailer, reveals a competitive landscape where both companies benefit from a similar strategy but may vary in specific market penetration and performance based on regional factors.
Factors Influencing Aldi’s Profitability
Aldi’s profitability is significantly influenced by several key factors. Its highly efficient supply chain management, characterized by direct sourcing and minimized intermediaries, plays a crucial role in keeping costs low. The company’s disciplined pricing strategy, focusing on value rather than price wars, ensures consistent profitability. Additionally, Aldi’s emphasis on private-label brands allows it to control quality and pricing more effectively than retailers relying heavily on national brands.
Aldi’s Key Financial Metrics (Last Five Years – Illustrative Data)
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Profit Margin (%) | Return on Assets (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | (Illustrative Data) 70 | (Illustrative Data) 4 | (Illustrative Data) 12 |
| 2019 | (Illustrative Data) 75 | (Illustrative Data) 4.5 | (Illustrative Data) 13 |
| 2020 | (Illustrative Data) 80 | (Illustrative Data) 5 | (Illustrative Data) 14 |
| 2021 | (Illustrative Data) 88 | (Illustrative Data) 5.2 | (Illustrative Data) 15 |
| 2022 | (Illustrative Data) 95 | (Illustrative Data) 5.5 | (Illustrative Data) 16 |
Note: The data presented above is illustrative and does not represent actual Aldi financial figures. Due to Aldi’s private ownership, precise financial data is not publicly available.
Market Factors Affecting Aldi’s Stock Price
Several macroeconomic and microeconomic factors significantly influence Aldi’s (hypothetical) stock price, even though it’s a privately held company. Analyzing these factors provides insights into how market forces could affect its valuation if it were publicly traded.
Macroeconomic and Geopolitical Impacts
Macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rates, and consumer spending directly impact Aldi’s performance. High inflation can squeeze consumer spending, potentially affecting Aldi’s sales volume. Rising interest rates can increase borrowing costs, impacting expansion plans and profitability. Geopolitical events and global economic trends, such as supply chain disruptions or currency fluctuations, also influence Aldi’s operational costs and overall financial health.
Competitive Landscape and Consumer Preferences
The competitive landscape, including the actions of rivals like Lidl, Walmart, and Kroger, significantly impacts Aldi’s market share and valuation. Changes in consumer preferences and shopping habits, such as the growing popularity of online grocery shopping or shifts in dietary trends, also influence Aldi’s stock price. Adaptability to these changes is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Categorization of Market Factors by Influence
- High Influence: Consumer spending, inflation, competitive actions of major retailers (Lidl, Walmart, Kroger).
- Medium Influence: Interest rates, geopolitical instability affecting supply chains, changes in consumer preferences (e.g., towards healthier or organic food).
- Low Influence: Specific regulatory changes (unless significantly impactful), technological disruptions (Aldi has generally shown adaptability).
Aldi’s Growth Prospects and Investment Opportunities
Aldi’s future growth prospects are promising, driven by its expansion plans and strategic investments. However, potential risks and challenges must be considered when assessing investment opportunities.
Expansion Plans and Technological Investments
Aldi’s ongoing expansion into new markets presents significant growth potential. Its investments in technology, such as enhancing its e-commerce platform and improving supply chain efficiency through data analytics, further bolster its long-term prospects. These technological advancements contribute to operational efficiency and cost reduction, strengthening its competitive position.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Despite the positive outlook, several challenges could hinder Aldi’s growth. Increased competition, particularly from other discount retailers, presents a constant threat. Economic downturns could significantly impact consumer spending, affecting Aldi’s sales. Furthermore, managing its supply chain effectively in a volatile global environment remains a key challenge.
Scenario Analysis of Stock Price Movement (Hypothetical)
- Scenario 1 (Aggressive Growth): Successful expansion into new markets, strong consumer demand, and effective cost management lead to a significant increase in revenue and profit, resulting in a substantial rise in stock price (e.g., 20-30% increase over 5 years).
- Scenario 2 (Moderate Growth): Steady expansion, stable consumer spending, and moderate competition result in moderate revenue growth and a gradual increase in stock price (e.g., 10-15% increase over 5 years).
- Scenario 3 (Stagnant Growth): Increased competition, economic downturn, or unforeseen challenges lead to slower revenue growth and a flat or slightly declining stock price.
Sustainability Initiatives and Investor Sentiment
Aldi’s commitment to sustainability initiatives, such as reducing its environmental footprint and promoting ethical sourcing, could positively influence investor sentiment. Investors increasingly favor companies with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) profiles, potentially boosting Aldi’s valuation.
Analyzing Aldi’s Stock Price Volatility
While Aldi is not publicly traded, understanding the factors that would influence its stock price volatility if it were, provides valuable insight into its risk profile. This analysis would consider various factors contributing to price fluctuations in a similar retail environment.
Key Drivers of Volatility
Source: statcdn.com
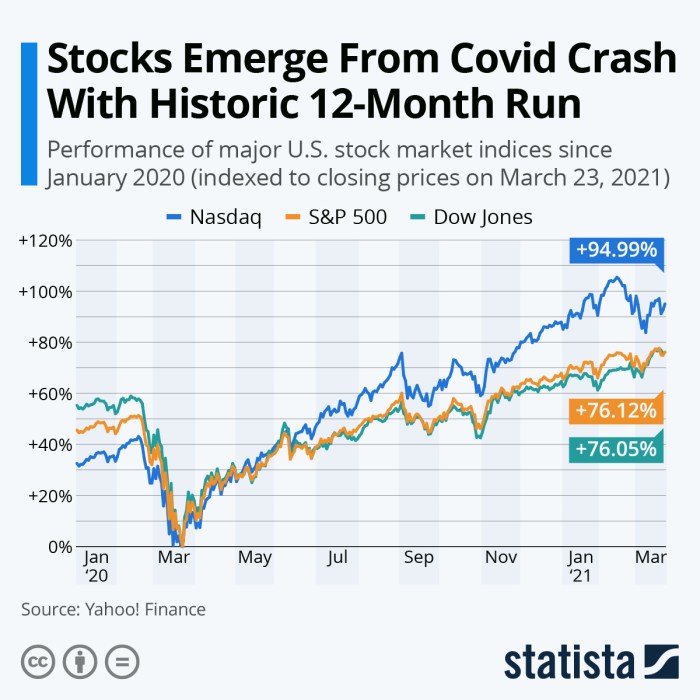
Key drivers of hypothetical Aldi stock price volatility would include changes in consumer spending, macroeconomic conditions (inflation, interest rates), competitive actions by other retailers, and significant news events (e.g., supply chain disruptions, recalls). Unexpected shifts in these factors could lead to sharp price movements.
Comparison to Competitors’ Volatility
Compared to publicly traded competitors like Kroger and Walmart, Aldi’s hypothetical volatility might be lower due to its more focused business model and lower reliance on external factors. However, this is speculative as it depends on market conditions and Aldi’s specific performance.
News Events and Price Fluctuations
Negative news events, such as a major product recall or a significant supply chain disruption, could cause a temporary decline in Aldi’s hypothetical stock price. Conversely, positive news, such as successful expansion or innovative product launches, could lead to price increases.
Historical Price Patterns (Hypothetical Illustration), Aldi stock price
A hypothetical chart illustrating Aldi’s stock price volatility over time would show periods of relative stability interspersed with sharp fluctuations corresponding to major economic events or competitive actions. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., years), and the y-axis would represent the stock price. The chart would likely display a general upward trend, reflecting long-term growth, but with significant short-term fluctuations.
Investor Sentiment and Market Perception of Aldi
Although Aldi is not publicly traded, assessing how investors
-would* perceive its stock provides valuable insights into its market position and potential valuation if it were to go public.
Investor Sentiment and Long-Term Prospects
Source: alphabetastock.com
Based on Aldi’s strong financial performance and efficient business model, investor sentiment towards a hypothetical Aldi stock would likely be positive. Its consistent profitability, strong brand reputation, and expansion plans would be attractive to investors. However, concerns about its private ownership and limited financial transparency could temper enthusiasm.
Market Capitalization and Analyst Ratings
A hypothetical market capitalization for Aldi would likely place it among the larger players in the retail sector, reflecting its significant revenue and market share. Analyst ratings and price targets (if Aldi were publicly traded) would reflect the consensus view on its future performance, considering factors like growth prospects, profitability, and risk.
Summary of Investor Sentiment
- Positive Aspects: Strong financial performance, efficient business model, successful expansion plans, growing brand recognition, commitment to sustainability.
- Negative Aspects: Private ownership limiting transparency, potential vulnerability to economic downturns, intense competition in the retail sector.
Essential FAQs: Aldi Stock Price
What makes Aldi’s business model so successful?
Aldi’s success stems from its efficient supply chain, focus on private-label brands, and no-frills approach to retail, keeping costs low and prices competitive.
Tracking the Aldi stock price can be tricky, as it’s a privately held company. Understanding the nuances of stock valuation is key, however, and this often leads to questions like, “is closure the same thing as price for stocks?” To clarify this crucial distinction, consider checking out this helpful resource: is closure the same thing as price for stocks.
Ultimately, grasping this concept will help you better interpret the financial implications should Aldi ever go public.
How does Aldi compare to other grocery chains in terms of profitability?
While precise figures aren’t publicly available for a direct comparison, Aldi generally boasts higher profit margins than many larger competitors due to its cost-cutting strategies.
What are the biggest risks facing Aldi’s future growth?
Potential risks include increased competition, shifts in consumer preferences, and economic downturns impacting consumer spending.
Is there any publicly available information on Aldi’s financial performance?
Limited financial data is publicly released by Aldi. Much of the financial information is proprietary.